Band Heaters
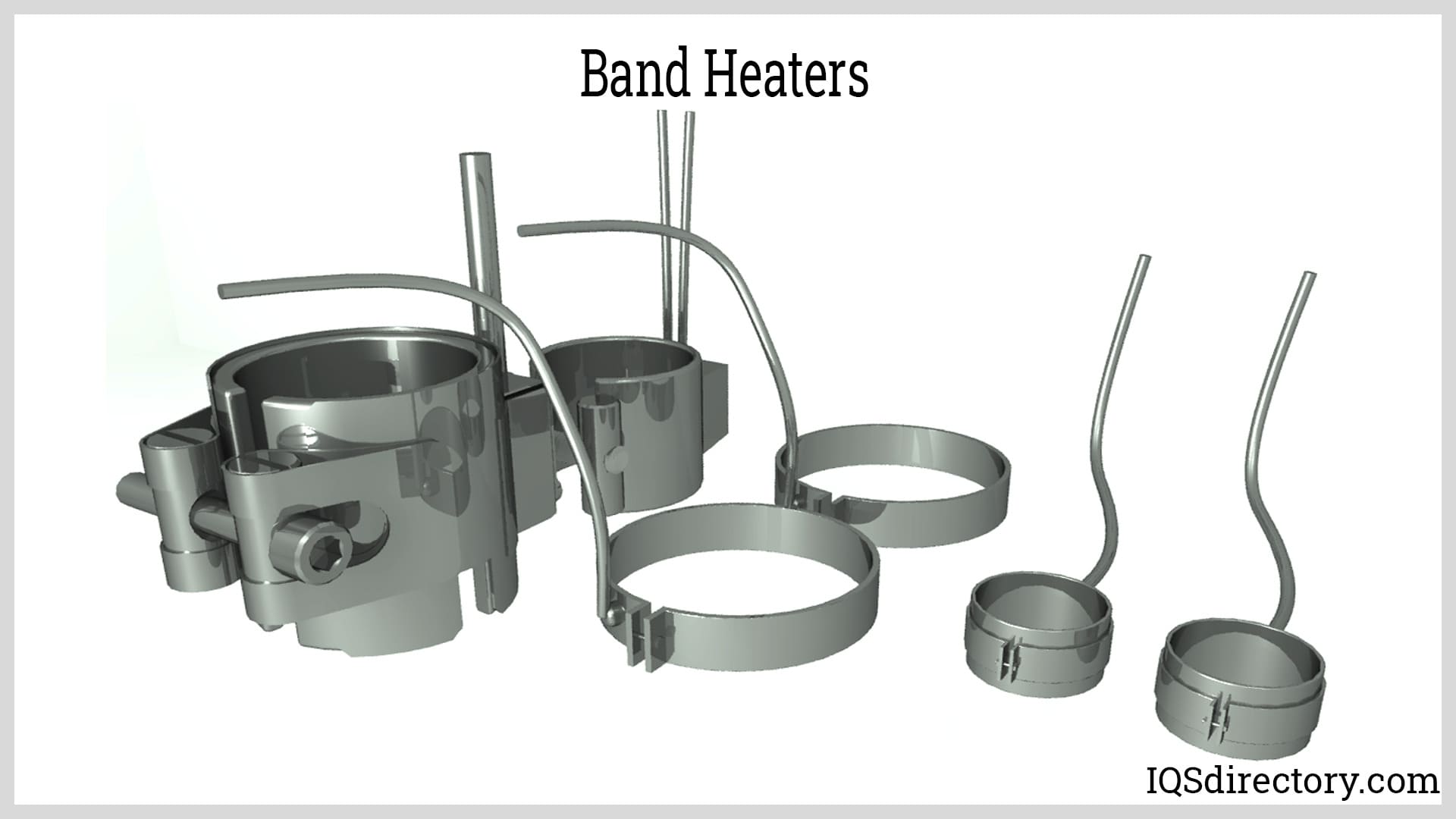

A band heater is a heating device that clamps onto objects to provide external heat using radiant and conductive heating. The different mounting methods of band heaters makes it possible to secure them tightly and firmly such that they do not shift or loosen…
Cartridge Heater
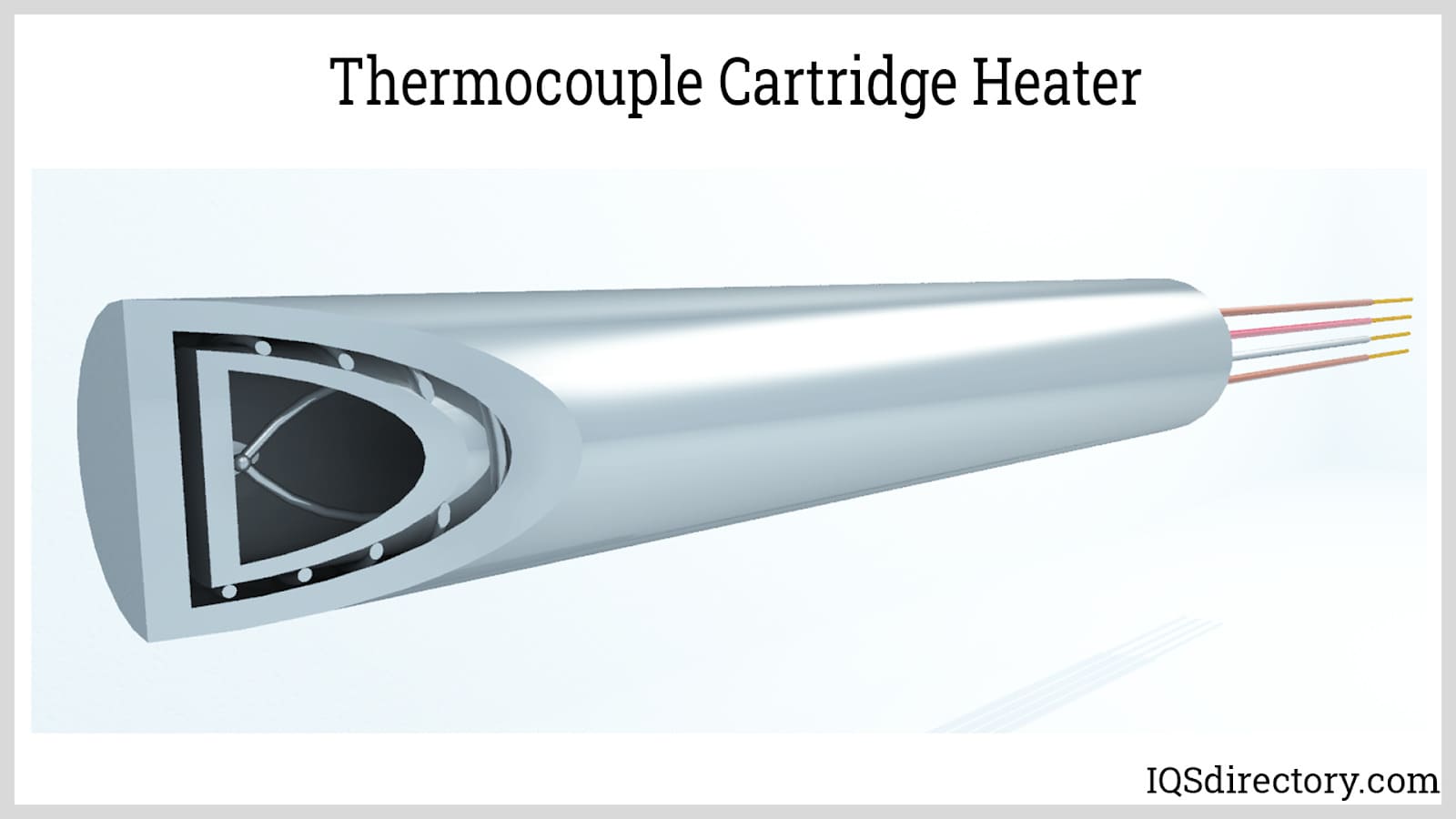
A cartridge heater is a cylindrical tubular heating device that provides concise and precise heating for various forms of materials, machinery, and equipment. Unlike an immersion heater, a cartridge heater is inserted into a hole in the item to be heated to furnish internal radiant heat…
Ceramic Heaters
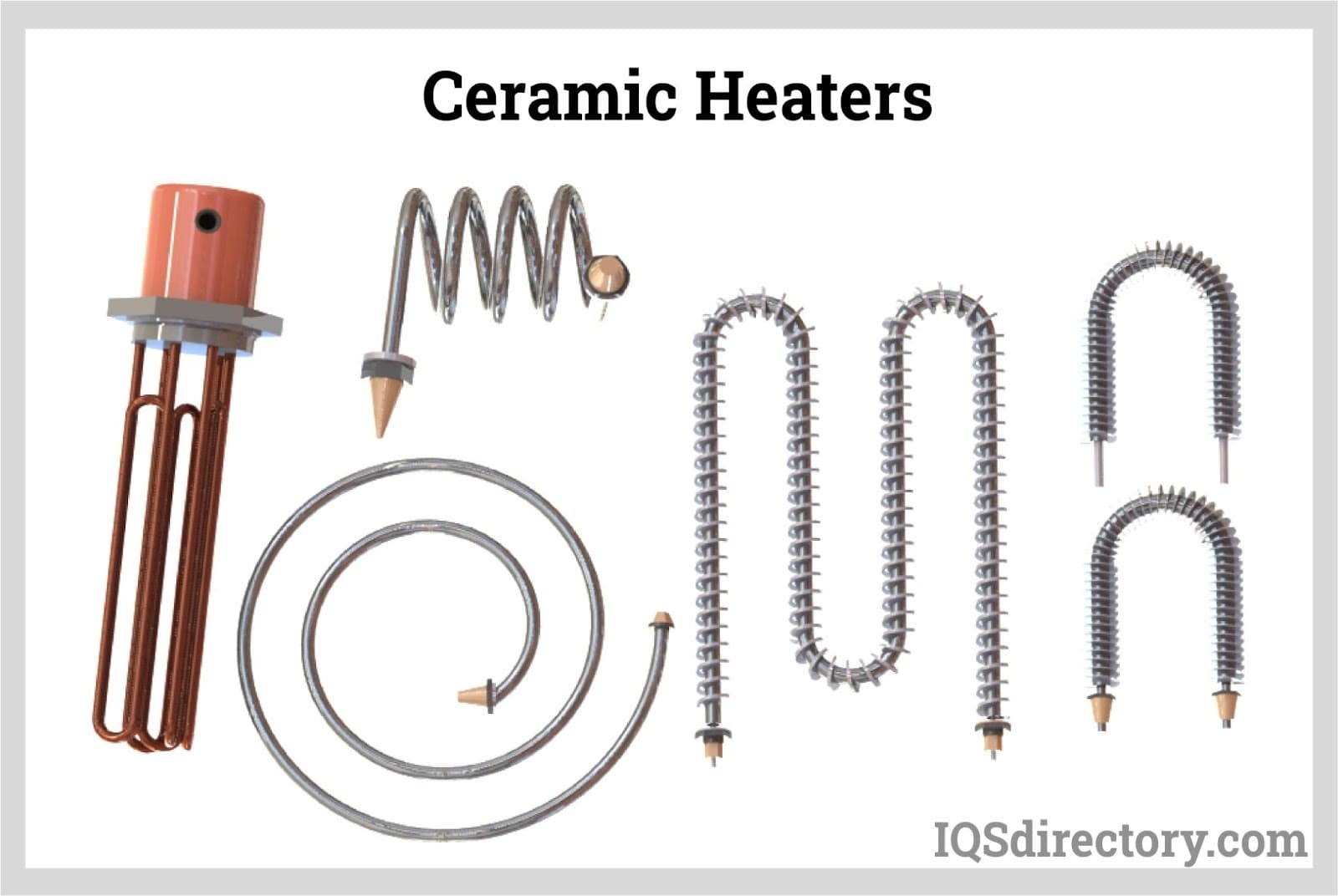
Ceramic heaters are electric heaters that utilize a positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic heating element and generate heat through the principle of resistive heating. Ceramic materials possess sufficient electrical resistance and…
Electric Heaters

Electric heating is produced by using a known resistance in an electric circuit. This placed resistance has very few free electrons in it so it does not conduct electric current easily through it. When there is resistance in…
Flexible Heaters
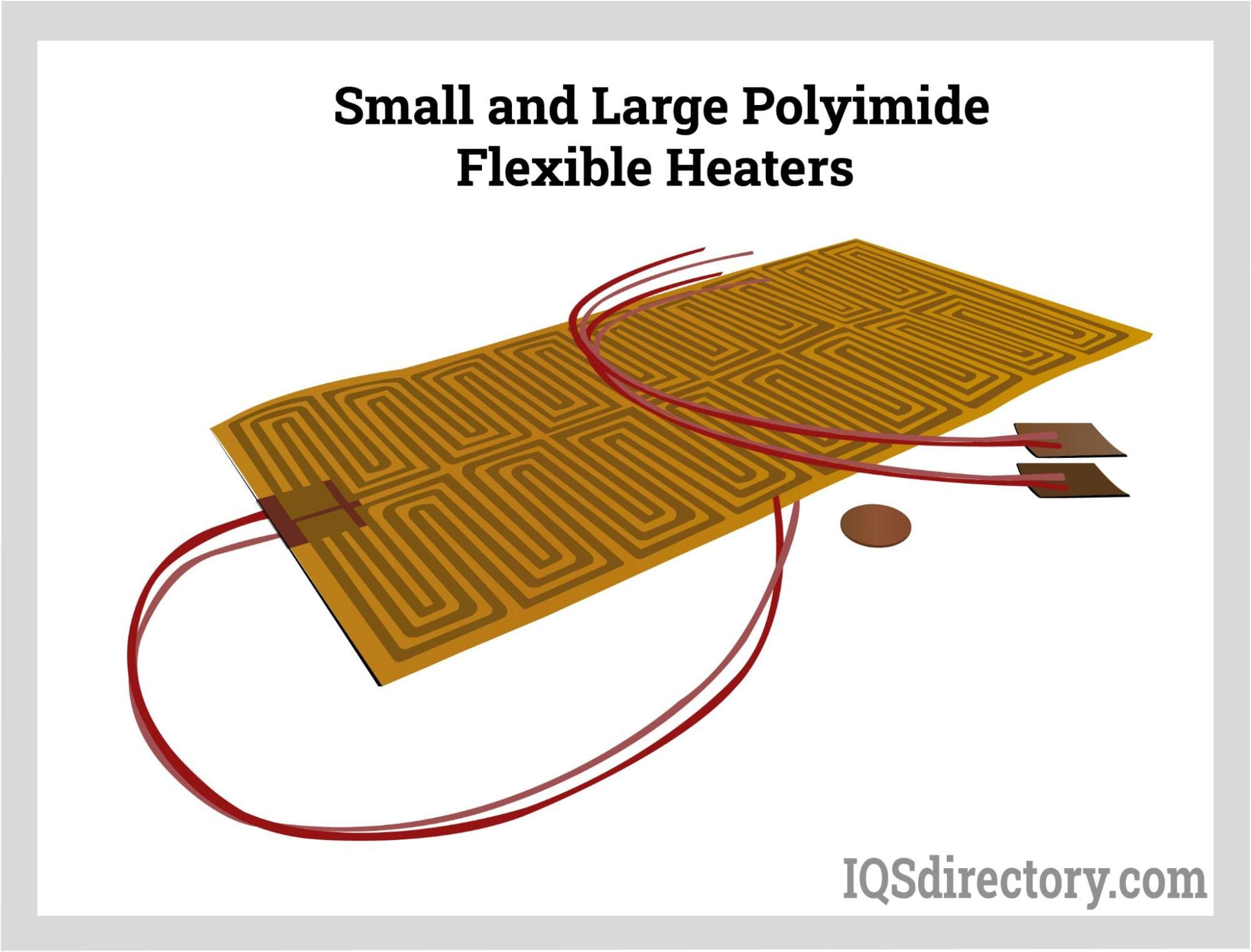
A flexible heater is a heater made of material that can bend, stretch, and conform to a surface that requires heating. The various forms of flexible heaters include polyimide film, silicone rubber, tape, rope, tank wrapping, gas cylinder, and ones that are designed…
Heating Element
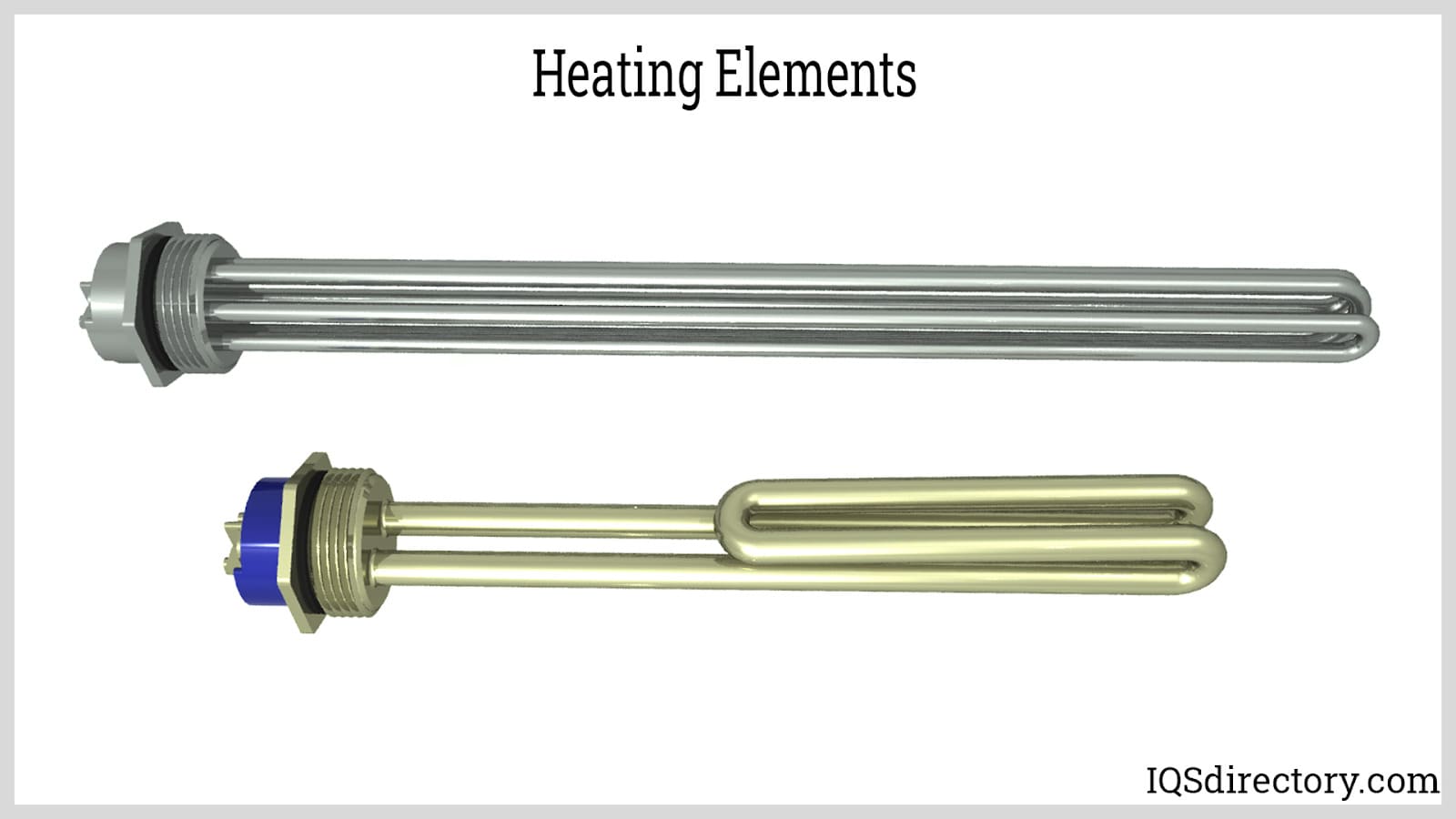
A heating element is a material or device that directly converts electrical energy into heat or thermal energy through a principle known as Joule heating. Joule heating is the phenomenon where a conductor generates…
Immersion Heaters
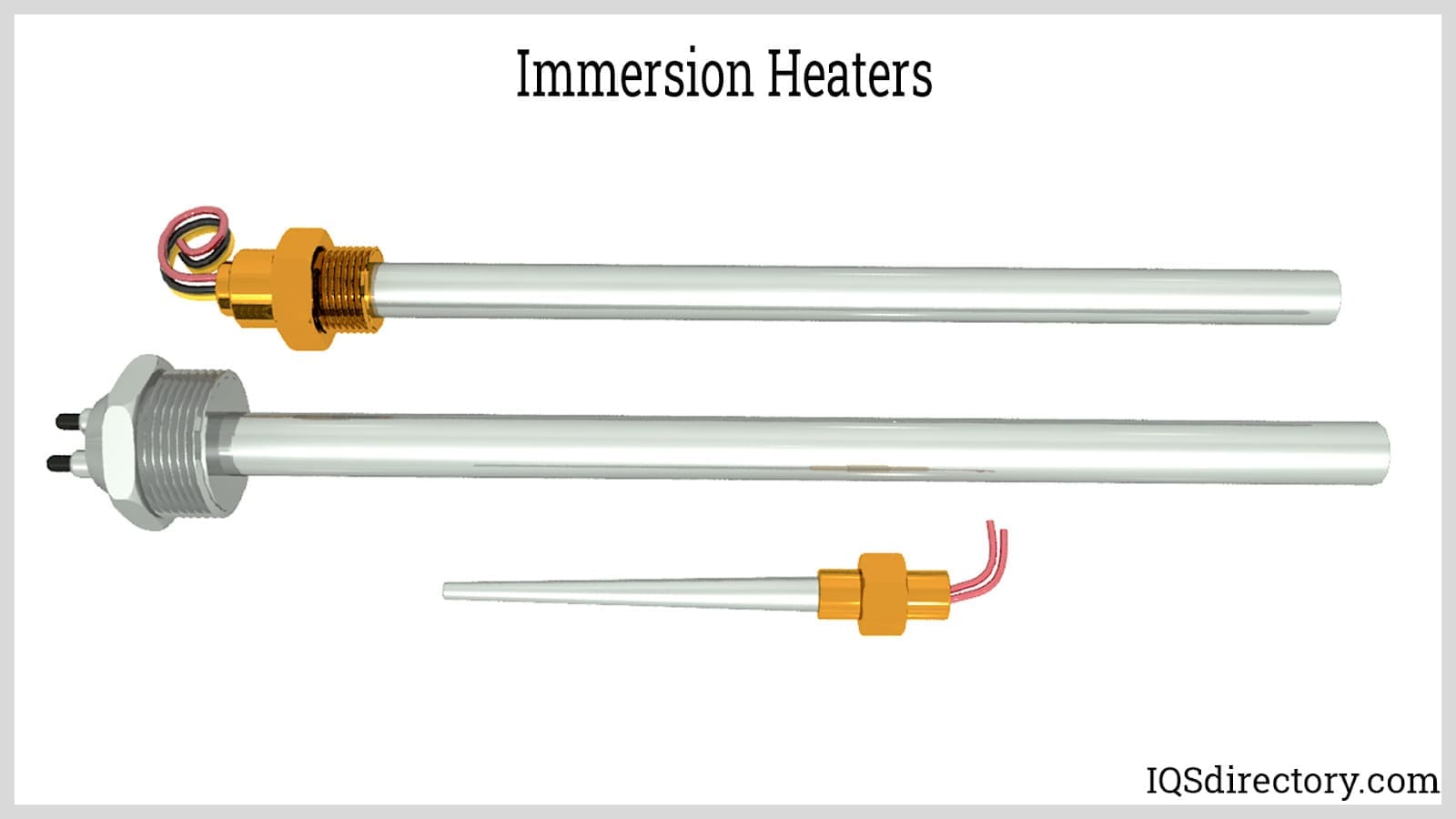
An immersion heater is a fast, economical, and efficient method for heating liquids in tanks, vats, or equipment. Known as bayonet heaters, they have heating elements that can be directly inserted into a container of water, oil, or other material in order to heat the entire contents…
Infrared Heating

Infrared heating is a heating method used to warm surrounding bodies by infrared radiation. Thermal energy is transferred directly to a body with a lower temperature through electromagnetic waves in the infrared region…
Radiant Heaters
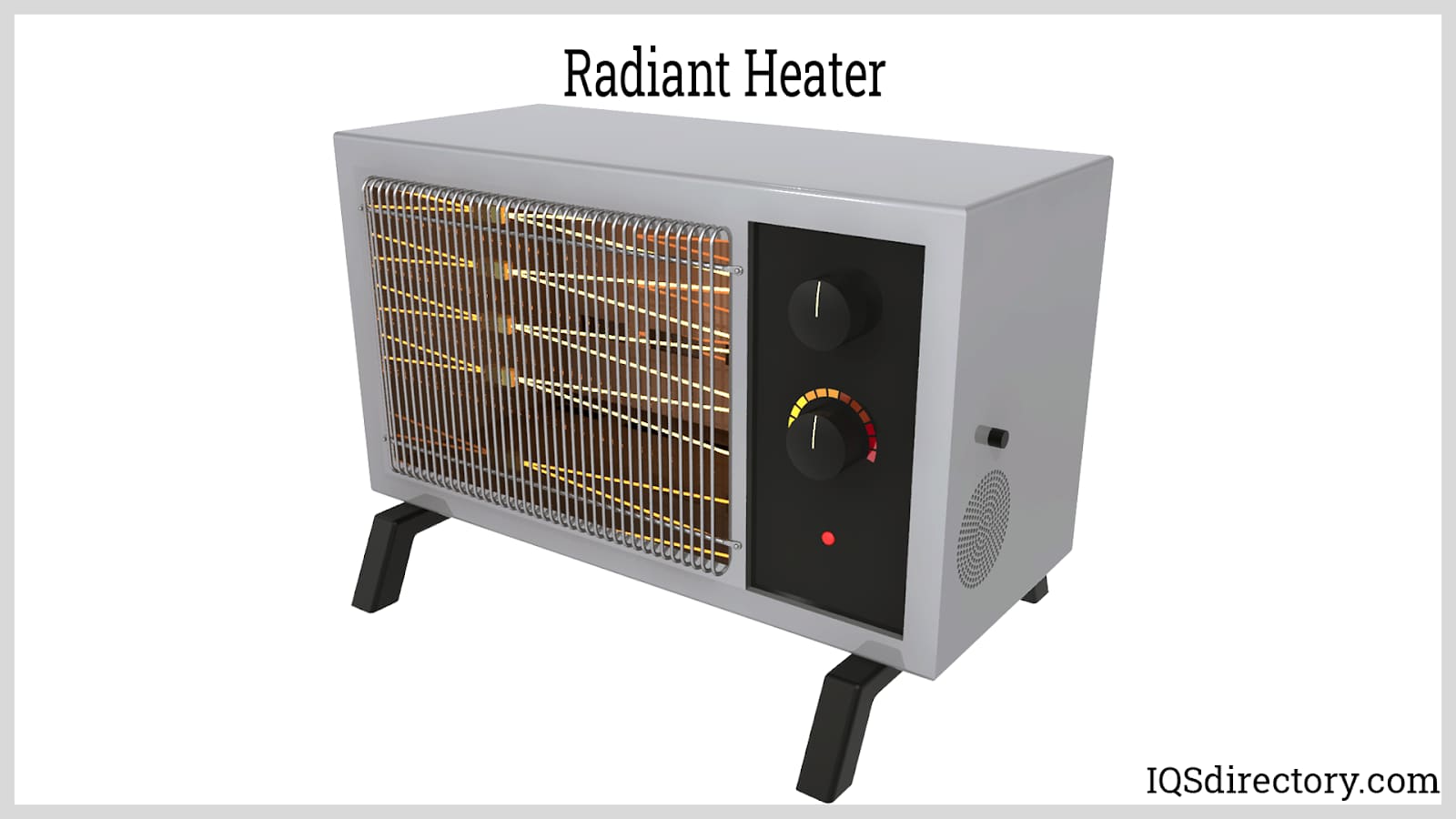

Radiant heaters are systems that generate heat internally and then radiate it to the nearby objects and people. The sun is a basic example of a radiant heater. When we feel warm on our bodies on a sunny day…
Types of Electric Heaters

The idea of an electric heater seems to be out of place in modern society since most buildings have a sophisticated central heating system. That may be true, but electric heaters can be a helpful way of saving energy while…
Heating Elements

A heating element is a material or device that directly converts electrical energy into heat or thermal energy through a principle known as Joule heating. Joule heating is the phenomenon where a conductor generates heat due to the flow of electric current…
Infrared Heaters
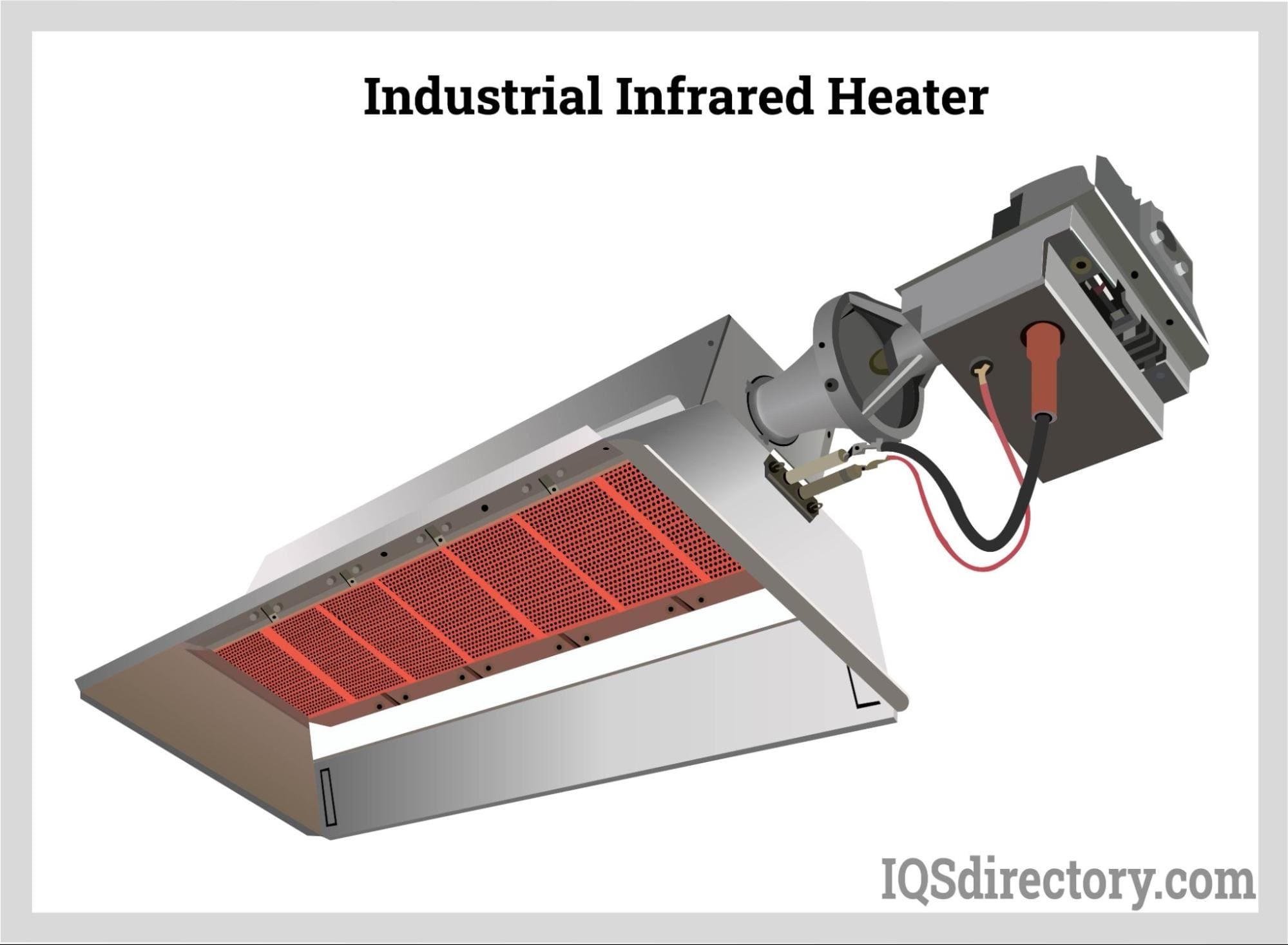
Infrared heating is a method for heating materials that uses electromagnetic waves to transfer energy from the infrared source to the product without heating the air in between. The emitted infrared energy is between 0.7 microns (µ) and 6 µ…
















 Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge Heaters Industrial Electric Heaters
Industrial Electric Heaters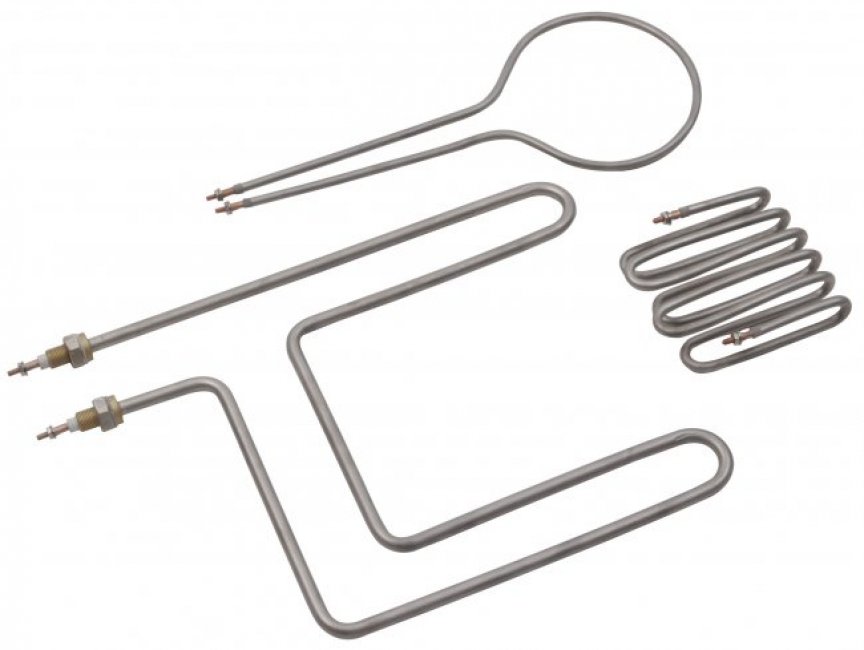 Heating Elements
Heating Elements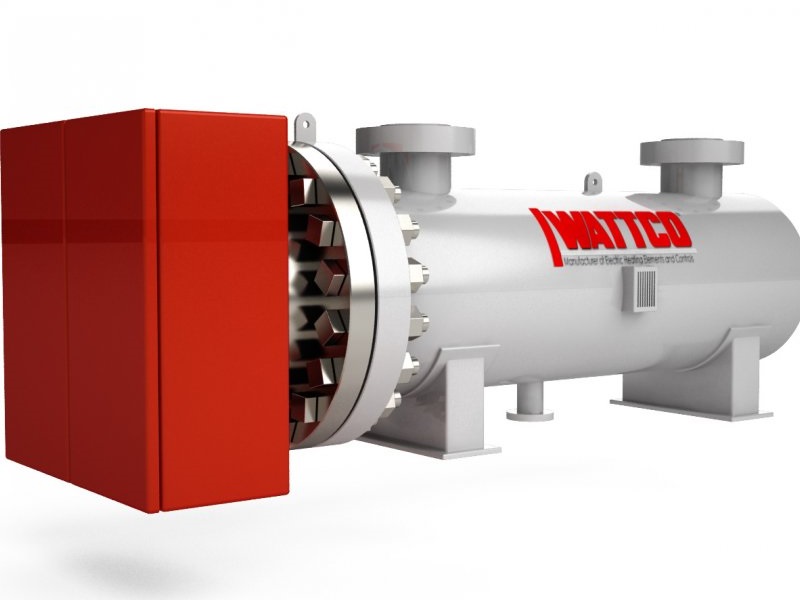 Immersion Heaters
Immersion Heaters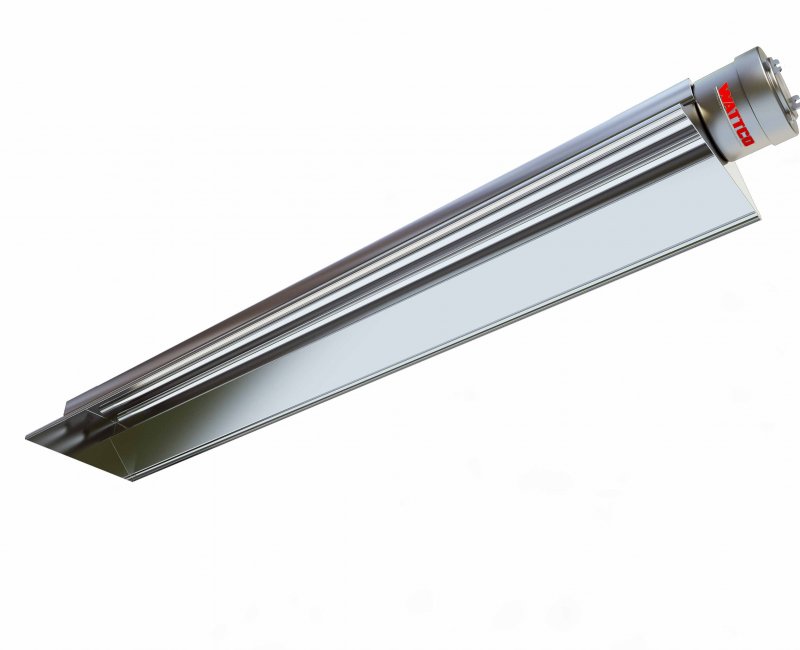 Infrared Heaters
Infrared Heaters Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services