A cartridge heater is a heating element in the shape of a tube that fits into drilled holes and is used in industrial activity. Cartridge heaters are extensively used in the heating process sector because they provide localized and accurate heating. Cartridge heaters are often used to heat a metal block from the inside, and they can be custom produced to a precise watt density based on the application’s requirement. Read More…
Backer Hotwatt is a superior designer & manufacturer of electric heaters and related heater accessories for various OEM & industrial applications.

At Cartridge Heaters Maxiwatt, we specialize in producing high-quality heating elements designed to meet the diverse needs of our clients across various industries. Our advanced heating elements are engineered with precision and built to last, providing reliable and efficient performance in even the most demanding applications. Utilizing cutting-edge manufacturing techniques and the finest...

At Dalton Electric Heating Co., Inc., we are proud to be a leading provider of high-performance electric heaters, serving various industries with innovative and reliable heating solutions. For decades, we have focused on designing and manufacturing durable products, including cartridge heaters, industrial heaters, and other custom thermal solutions, all built to meet the most demanding industrial ...

At Ryan Herco Flow Solutions, we take pride in providing high-performance fluid handling and filtration products, and our electric heaters stand out as an essential part of that mission. We specialize in electric heating solutions designed to deliver precise temperature control, reliability, and safety across a wide range of applications
More Cartridge Heater Manufacturers
Cartridge heaters are high-efficiency, industrial electric heating elements engineered for precise temperature control in a wide range of applications. An exterior metal shell, known as a sheath, surrounds the heating element. This shell is usually stainless steel and includes an insulator and a coil of nickel-chromium heater wiring. A standard electrical connection is found on most cartridge heaters; there are, however, different cable designs available, such as right-angle exit, fastening tab, and flange mounting, to mention a few.
Searching for high-performance electric heating solutions for your manufacturing or processing needs? Cartridge heaters are among the most reliable and customizable options for industrial heating, providing consistent, energy-efficient results.
Looking to understand how cartridge heaters work, what their benefits are, or which type to choose for your application? Explore our detailed guide below to find answers to common questions and discover best practices for selecting, installing, and maintaining industrial cartridge heaters. Whether your goal is to improve process efficiency, ensure product quality, or comply with safety regulations, understanding cartridge heater technology can help inform your purchase decision.

Salient Features of Cartridge Heaters
- Constructed from corrosion-resistant materials for longevity and reliable operation, making them ideal for use in corrosive or chemical environments where durability is crucial. Electric cartridge heaters are often specified for demanding industrial settings such as chemical processing plants and food production lines.
- Explosion-proof heaters are available, engineered to withstand explosive environments and safeguard both the contents and surrounding area. Some specialized providers offer heaters with spark- and flame-resistant housings, suitable for hazardous locations.
- Fitted with a grounding wire, cartridge heaters can attach the electrical wiring to a common ground, effectively dispersing electrical load in the event of a short circuit—an essential safety feature for industrial heating equipment.
- Integrated temperature detectors enable real-time monitoring of the heater’s temperature during operation. This allows for precise thermal control, reduces the risk of overheating, and ensures consistent product quality in temperature-sensitive processes.
- UL and CSA certifications are standard for many cartridge heating elements, offering assurance of compliance with international safety and performance standards.
- Cartridge heaters support extreme temperatures, offering heat output of up to 1562 °F (850 °C) and can operate at voltages up to 600V, making them suitable for a variety of high-temperature applications.
- The maximum surface load provided by cartridge heaters is 35 W/cm², allowing for efficient heat transfer when installed with a close fit in drilled holes or metal blocks.
What Makes Cartridge Heaters a Preferred Industrial Heating Solution?
Buyers evaluating industrial heating solutions are often drawn to cartridge heaters due to their compact form factor, precision temperature control, rapid heat-up times, and ease of installation. Their versatility allows for customization in length, diameter, watt density, voltage, and termination, making them adaptable to a wide range of heating requirements in manufacturing, laboratory, and process environments. Many industries, including plastics, packaging, medical device manufacturing, food processing, and semiconductor fabrication, rely on cartridge heaters for their critical processes.
Why choose cartridge heaters over other industrial heating elements? Their robust construction and efficient heat transfer make them a top choice for engineers seeking high reliability, fast thermal cycling, and minimal downtime. If you need a heating solution that performs consistently in harsh environments, cartridge heaters should be at the top of your list.
Materials Used in Cartridge Heaters
The performance, durability, and efficiency of a cartridge heater depend heavily on the materials used in its construction. A typical cartridge heater is comprised of four primary components, each with different material options tailored to specific application requirements. Understanding the material options and their respective benefits is crucial for selecting the right cartridge heater for your industrial, commercial, or laboratory application.
Sheath and Sleeve Materials
Jackets, sheaths, or sleeves serve as protective exterior coverings for the heating components. Sleeve materials used in cartridge heaters are often selected for their thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Common sheath materials include:
- None: The heater has a bare and exposed heating element that does not contain a sheath or sleeve. This option is rarely used in industrial settings due to safety and durability concerns.
- Stainless Steel: A chemically and corrosion-resistant alloy with high-pressure ratings, stainless steel sheaths are the industry standard for most cartridge heaters, especially in food processing, medical, and chemical industries.
- Aluminum: Known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, high reflectivity, and oxidation resistance. Aluminum sheaths are used in applications where rapid heat transfer and lightweight construction are priorities.
- Nickel Alloy: Offers superior corrosion resistance and is commonly used in specialized environments exposed to acids, alkalis, or high humidity. Inconel and other nickel alloys are ideal for high-temperature, high-stress applications.
- Copper, Iron, Steel, Brass: These materials are chosen for specific industrial needs, such as enhanced thermal transfer (copper), strength (steel), or cost-effectiveness (brass).
When evaluating sheath options, consider the chemical compatibility, temperature requirements, and physical stresses of your process environment. For example, stainless steel is often specified for sanitary or food-grade applications, while Inconel is preferred in aggressive chemical processing or high-temperature furnace operations.
Insulation Materials
The insulation layer separates the resistance coil from the sheath, ensuring electrical safety and efficient heat transfer. Common insulation materials include:
- Fiberglass: Sturdy, long-lasting, and resistant to chemicals and high temperatures; frequently used for lead wires and as a flexible insulation layer in industrial cartridge heaters.
- Ceramic: Made from nonmetallic materials such as clay, ceramics are fired at high temperatures to create a heat- and chemical-resistant barrier. Ceramic insulation is often specified for applications requiring rapid heat response and superior thermal stability.
- Mica or Mineral Insulation: Offers excellent electrical insulation and heat transfer properties for medium- to high-temperature applications.
- Magnesium Oxide (MgO): Provides a high melting point (5072 °F [2800 °C]), outstanding temperature resistance (3092 °F [1700 °C] in reducing, 4172 °F [2300 °C] in oxidizing atmospheres), and is the most common insulation for cartridge heaters in demanding environments.
- Fluoropolymer: Used in specialized applications requiring chemical inertness and flexibility.
Looking for optimal insulation for high-temperature cartridge heaters? Magnesium oxide is the preferred choice for most high-watt density, high-reliability applications, offering both excellent dielectric strength and thermal conductivity.
Electrical Connection and Termination Options
The electrical connection in a cartridge heater can be customized to suit the installation environment and application. Termination options include:
- Armor cable leads for mechanical protection and durability.
- Screw terminal boxes for secure connections in industrial machinery.
- Metal braided leads for flexibility and resistance to abrasion.
- Insulated leads for electrical safety in challenging environments.
- Bare leads for applications where direct wiring is preferred.
- Plugs and quick disconnects for rapid installation and maintenance.
Need help choosing the right termination? Consider your installation environment, maintenance needs, and the level of protection required for your wiring.
Mounting Options
Cartridge heaters can be mounted using various systems such as locating rings, threaded pipe fittings, and mounting flanges. The choice of mounting method depends on the process equipment, space constraints, and ease of replacement.
For high-watt density applications or when using cartridge heaters in high-vibration machinery, robust mounting hardware is essential for safety and performance.
Construction of Cartridge Heaters
The robust construction of cartridge heaters is engineered for performance, longevity, and adaptability across a spectrum of industrial heating applications. The construction process consists of seven key parts:
- Heating Coil: The core component where electrical resistance generates heat. Nichrome (nickel-chromium alloy) is the most common material due to its high melting point, electrical resistance, and stability at elevated temperatures.
- Insulation: Prevents electrical contact between the coil and the sheath, thus avoiding short circuits. Magnesium Oxide (MgO) is typically used in industry for its superior heat conductivity and dielectric strength.
- Sheath: The outer covering that makes direct contact with the material or substance to be heated, designed for optimal heat transfer and protection of internal elements.
- Sealing: A seal is applied to the open end of the cartridge to prevent the coil and insulation from escaping and to block contaminants such as dust, air, or moisture from entering the heater assembly.
- Termination: Cartridge heaters are adaptable for various industrial applications, with options for straight, right-angle, and custom lead orientations to facilitate installation and wiring.
- Lead Wire Type: Typically, fiberglass-insulated lead wires are used for high-temperature industrial applications. Other options include Teflon or silicone insulated wires for environments with specific chemical or flexibility requirements.
- Watt Density: Defined as the amount of heat generated per unit surface area, watt density is selected based on the thermal load required for the specific industrial process. High watt density cartridge heaters are used for applications demanding rapid heat-up and high energy output, while low watt density models are preferred for sensitive materials or slow, uniform heating.
Why is robust construction important in cartridge heaters? Quality construction ensures consistent performance, safety, and a long operational life, even under rigorous thermal cycling and hostile industrial conditions.


How Does a Cartridge Heater Work?
Curious about the operating principles and efficiency of cartridge heaters? Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a cartridge heater functions:
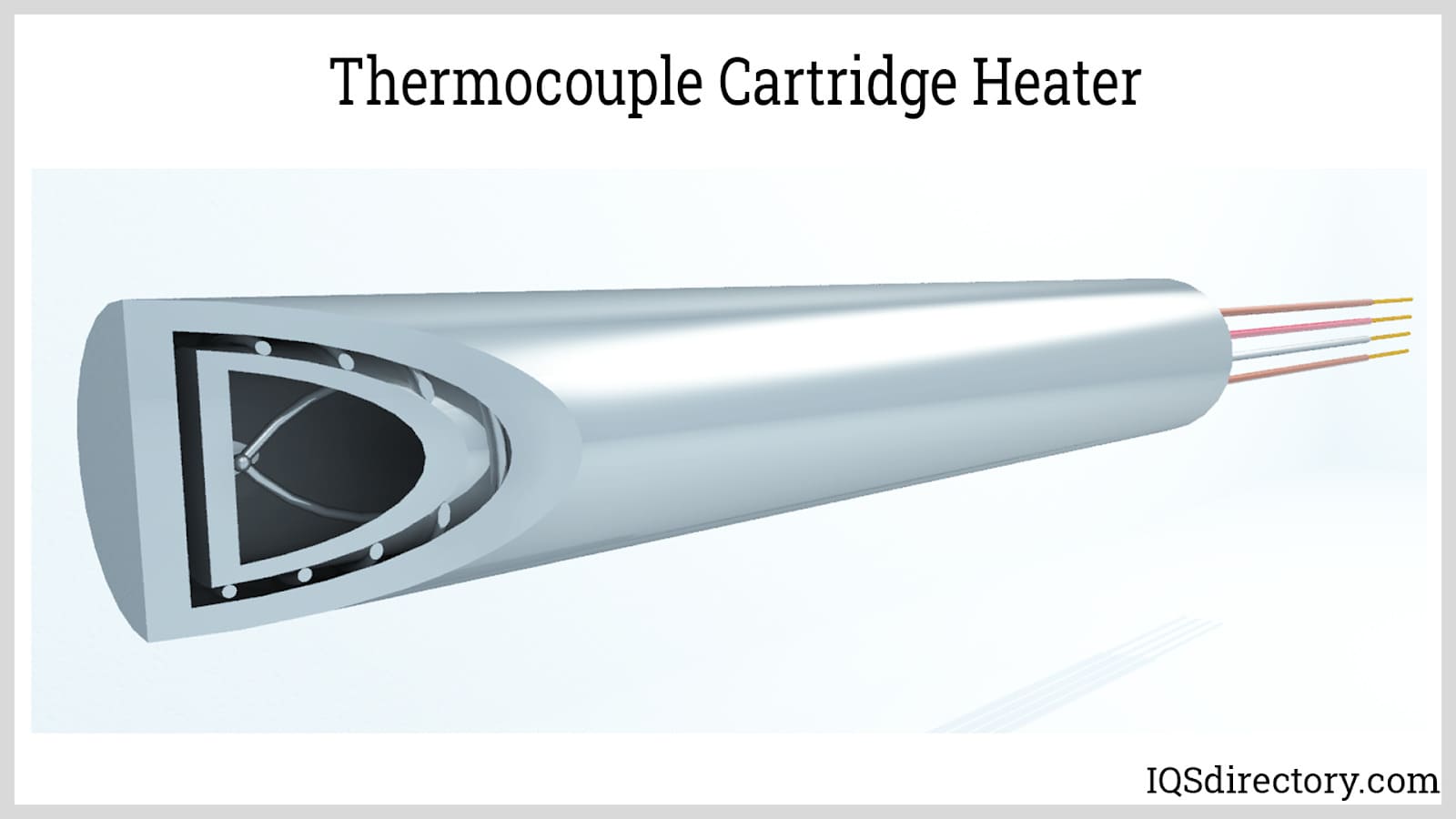
- A cartridge heater comprises a resistance coil wound around a ceramic or magnesium oxide core and encased in a metal sheath. The design ensures uniform heating and efficient thermal transfer.
- When electrical power is supplied, current flows through the resistance coil, generating heat according to Joule’s law. The sheath rapidly heats up, transferring thermal energy to the surrounding material, such as a metal block, mold, or liquid.
- The heat generated is then transferred to the material or component in direct contact with the heater, allowing for precise temperature control and rapid heat-up times.
- Advanced models incorporate built-in temperature sensors or thermocouples for real-time monitoring, automatic shutoff, or integration with process control systems.
Looking for information on energy efficiency or troubleshooting common cartridge heater issues? Explore our FAQs or contact a cartridge heater supplier for expert advice on optimizing heater performance in your facility.
Have questions about the best way to control cartridge heater temperatures? Learn more about integrating cartridge heaters with precise temperature controllers, thermocouples, and process automation for optimal safety and performance.
Applications of Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge heaters are widely used across multiple industries for their reliability, versatility, and rapid heat-up characteristics. They are specifically designed to heat metal molds, dies, platens, and various metal components in the metalworking industry. Key applications include:
- Lamination Processes: Ensuring uniform heat distribution critical for bonding layers of material in furniture, automotive, and electronics manufacturing.
- Medical Equipment: Providing precise temperature control for sterilization, fluid heating, and laboratory instrumentation.
- Molding of Plastic: Used in injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding machines to maintain optimal processing temperatures and improve product consistency.
- Molds for Hot Runners: Delivering localized heating for hot runner systems in plastic injection molding, reducing cycle times and enhancing part quality.
- Wafer Processing for Semiconductors: Offering clean, high-temperature heating required for wafer fabrication, lithography, and bonding processes in the semiconductor industry.
- Heating Liquids and Gases: Providing efficient, direct heating for tanks, pipes, and vessels in chemical processing, food and beverage, and laboratory applications.
- Packaging Machinery: Used to maintain consistent sealing and cutting temperatures for faster production speeds and reduced downtime.
- Food Production: Ensuring food safety and product quality by supplying controlled heat for cooking, baking, or sterilization equipment.
- Die Casting and Metal Forming: Maintaining consistent mold and die temperatures for improved part quality and reduced scrap rates.
- HVAC and Thermal Management: Used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for localized heat in valves, dampers, and fluid lines.
- Scientific Research: Supporting laboratory heating needs, including sample incubation, reaction vessel heating, and material testing.
Want to discover the best cartridge heater for your specific industry or application? Browse our directory of cartridge heater manufacturers or contact our expert team for tailored recommendations.
How do industries maximize the value of cartridge heaters? By selecting the right watt density, sheath material, and control system, industries optimize process speed, reduce energy consumption, and ensure product quality.

Benefits of Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge heaters offer a range of benefits that make them the preferred choice for industrial, commercial, and laboratory heating applications:
- Compact Design: Allows for installation in confined spaces and intricate machinery layouts. Their cylindrical shape fits snugly into drilled holes for optimal heat transfer.
- High Watt Density: Capable of delivering significant heat output in a small footprint, increasing process efficiency and reducing warm-up times.
- Customizable Configurations: Available in various lengths, diameters, voltages, and termination styles to meet specific requirements.
- Rapid Response: Heaters reach operating temperature quickly, minimizing downtime and improving productivity.
- Reliable and Long-Lasting: Constructed from durable materials for extended service life, even in harsh industrial environments.
- Precise Temperature Control: Integration with sensors and process controllers for accurate thermal regulation, essential in quality-critical manufacturing processes.
- Versatility: Suitable for direct and indirect heating of solids, liquids, and gases across a broad spectrum of industries.
- Energy Efficiency: Direct contact with the material to be heated minimizes energy loss and reduces operational costs.
- Safety Features: Built-in grounding wires, temperature sensors, and certified designs (UL, CSA) reduce the risk of accidents and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Low Maintenance: With proper installation and controls, cartridge heaters require minimal maintenance, reducing the total cost of ownership.
- Wide Temperature Range: Suitable for applications requiring both moderate and extreme temperatures, enhancing application flexibility for engineers and designers.
Looking for a heating solution that balances efficiency and safety? The advanced engineering of cartridge heaters provides both, making them a reliable choice for modern industrial heating demands.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Cartridge Heater
Selecting the right cartridge heater involves more than just choosing the correct size and wattage. Here are key decision factors for buyers and engineers:
- Operating Temperature: Ensure the heater’s maximum temperature rating aligns with your application’s requirements.
- Watt Density: Match the watt density to the material, application, and required heat-up speed. High watt densities are ideal for rapid heating, while lower densities are better for sensitive materials or applications requiring slow, uniform heating.
- Sheath Material: Select a sheath material compatible with your process media (e.g., stainless steel for food and medical, Inconel for corrosive chemicals).
- Voltage and Power Requirements: Verify compatibility with facility electrical systems and controls.
- Length and Diameter: Choose dimensions to ensure a snug fit in the drilled hole or mounting location for efficient heat transfer.
- Termination Style: Pick the appropriate electrical termination for ease of installation, maintenance, and safety.
- Environmental Considerations: Consider exposure to moisture, vibration, chemicals, or dust, and select heaters with appropriate IP ratings or protective features.
- Certifications and Safety Standards: UL, CSA, CE, or ATEX certifications may be required depending on your industry or location.
- Customization Needs: Many manufacturers offer custom cartridge heaters tailored to unique specifications. Consider consulting with an expert for specialized or high-volume applications.
Not sure which cartridge heater suits your process?
- What watt density do I need for heating aluminum molds?
- Should I choose a high- or low-watt density heater for my food processing application?
- How do I select the right sheath material for chemical resistance?
How do I compare cartridge heater brands and models? Look for technical datasheets, customer testimonials, and after-sales support availability. Use product selectors and comparison charts to evaluate key specs, warranty terms, and compatibility with your process controls.
Installation, Maintenance, and Troubleshooting
Proper installation and ongoing maintenance are critical for maximizing the performance and lifespan of cartridge heaters. Here are some best practices:
- Installation: Ensure a tight fit in the drilled hole for optimal heat transfer. Use thermal grease if recommended by the manufacturer. Avoid bending lead wires excessively to prevent damage.
- Wiring: Follow all electrical codes and use proper terminal connections. Verify that the supply voltage matches the heater’s specifications.
- Temperature Control: Integrate sensors and controllers for precise monitoring and automatic shutoff in case of overheating.
- Routine Inspection: Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or electrical insulation breakdown. Replace heaters showing signs of damage.
- Troubleshooting: Common issues include uneven heating, premature failure, or blown fuses. These can often be traced to poor fit, over-voltage, inadequate temperature control, or contamination. Consult your heater supplier for detailed troubleshooting guides.
- Preventive Maintenance: Implement scheduled maintenance protocols, including cleaning, electrical testing, and calibration of control systems to minimize unscheduled downtime and extend heater life.
- Monitoring System Integration: For facilities with advanced process automation, integrate cartridge heater monitoring into your SCADA or building management system for predictive maintenance and real-time fault alerts.
Wondering how to extend the service life of your cartridge heater or reduce downtime? Explore our maintenance resources or request support from our technical team.
What are the key signs a cartridge heater needs replacement? Watch for issues such as slow heat-up, visible sheath damage, or tripped breakers. Frequent replacement may indicate a need to review your process controls or heater selection.
Choosing the Correct Cartridge Heater Manufacturer
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing a cartridge heater from a cartridge heater manufacturer, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of cartridge heater manufacturers. Each cartridge heater company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each cartridge heater business website using our patented website previewer for a better idea of what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple cartridge heater businesses with the same form.
Ready to compare cartridge heater suppliers? Browse our directory, request quotes, and make an informed decision based on capabilities, certifications, lead times, and support services.
Still have questions? Check our FAQs or contact us for personalized guidance on selecting, specifying, or troubleshooting cartridge heaters for your unique application.
Looking for additional information on related electric heating technologies? Explore our in-depth resources on immersion heaters, tubular heaters, flexible heating elements, and process temperature control solutions for the complete picture on industrial heating options.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Cartridge Heaters
- What is the typical lifespan of a cartridge heater? Depending on application and maintenance, cartridge heaters can last several years. Proper fit, voltage settings, and protection from contamination extend service life.
- Can cartridge heaters be used with temperature controllers? Yes, most industrial cartridge heaters are compatible with digital temperature controllers, thermocouples, or RTDs for precise process control.
- Are there cartridge heaters for hazardous or explosive environments? Explosion-proof cartridge heaters with certified housings and terminations are available for hazardous area heating.
- What is the difference between high and low watt density cartridge heaters? High watt density heaters deliver more heat per square inch, ideal for rapid heating of metals. Low watt density models are better for gentle heating or where temperature-sensitive materials are involved.
- Can I get custom cartridge heater designs? Leading manufacturers offer custom heaters with specific wattages, lengths, diameters, and termination configurations to fit unique process requirements.
- How do I prevent premature cartridge heater failure? Ensure proper fit, voltage accuracy, clean installation environments, and regular maintenance to avoid common failure causes such as contamination or electrical overload.
Need personalized advice or a quote? Contact our team for application engineering support, custom design options, or help with large-scale procurement of cartridge heaters and other industrial heating elements.










 Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge Heaters Industrial Electric Heaters
Industrial Electric Heaters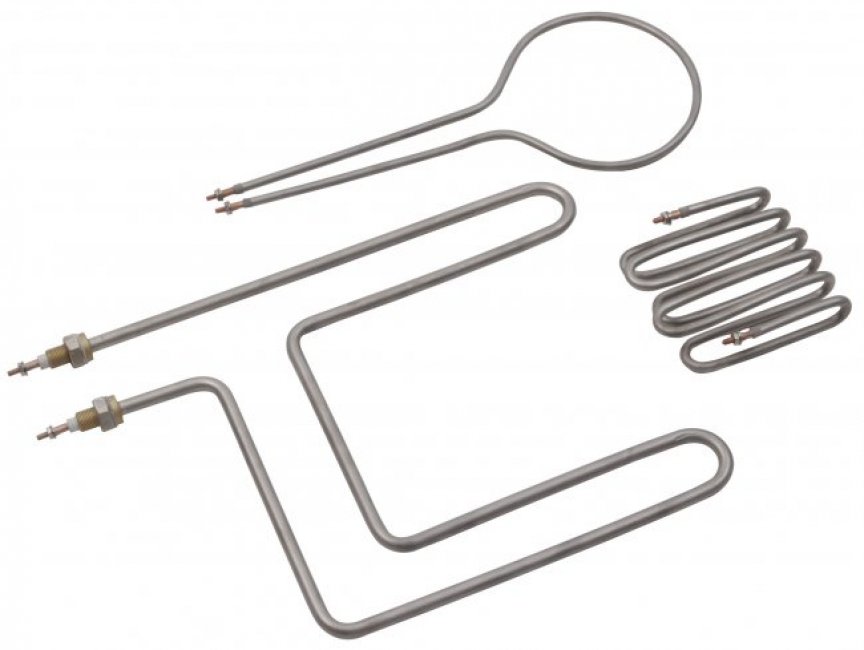 Heating Elements
Heating Elements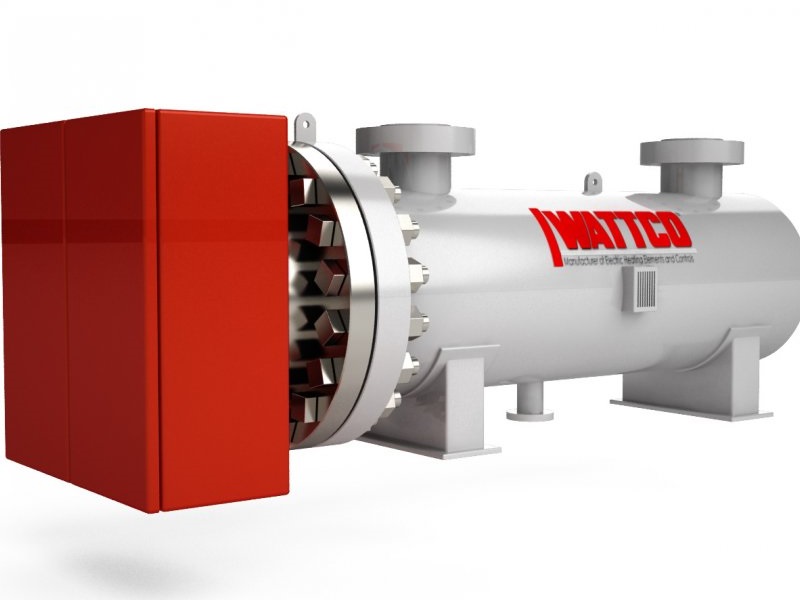 Immersion Heaters
Immersion Heaters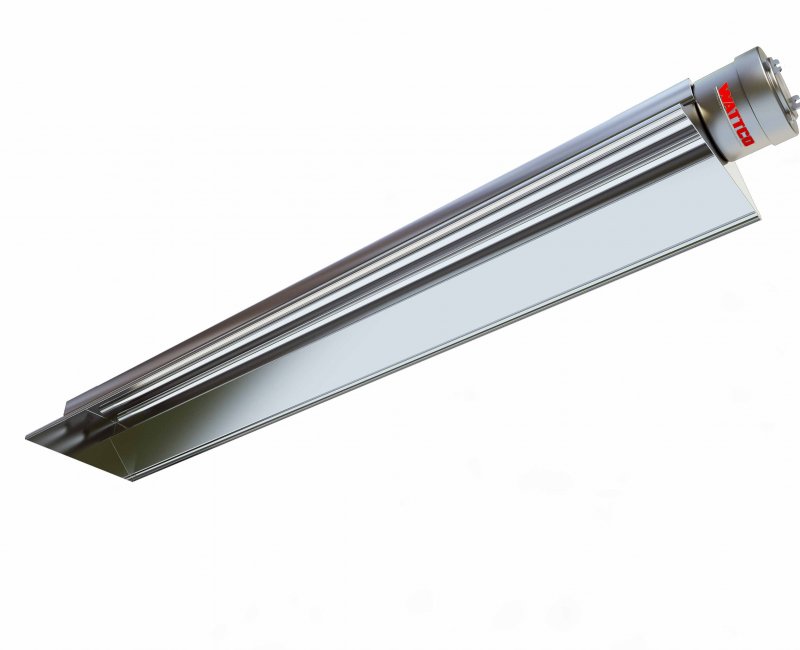 Infrared Heaters
Infrared Heaters Air Conditioners
Air Conditioners Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services